Close Menu
-
ENGAGEMENT RINGS
- Engagement Ring Style
- Shape
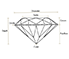
- Diamonds
- Metal
- Our Guide to
-
WEDDING RINGS
- Ring Style
- Metal
- Our Guide to
-
LOOSE DIAMONDS
- Diamond
- Design Your Own
- Our Guide to
-
JEWELLERY
- Earrings
- Pendants
- Shape
-
Diamonds
-
Design Your Own
-
- Earrings
- Pendants
- Jewellery Buying Guide
- Bespoke
-
About Us
- On Products
- On Diamond
- On Services
Our Guarantee